Introduction
Autonomous Vehicles are self-driving vehicles that use a combination of sensors, cameras, artificial intelligence (AI), and advanced algorithms to navigate and operate without human intervention.
In the world of autonomous and semi-autonomous vehicles, Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) are at the heart of enhancing vehicle safety and user experience. As ADAS technologies evolve, so do the components that support their development and testing, like Scenarios, Maps, and Simulators. For testing an autonomous vehicle (AV), scenarios define specific elements such as speed and lane operations. Maps play a crucial role in scenarios, as they allow scenarios to be applied within a given context. Testing on appropriate simulators ensures the accuracy and effectiveness of both the scenarios and maps. However, use of realtime streaming maps (as provided by Here maps using protocols like ADAS RP) is not cost effective. As a result, there is a lot of focus on creating and using synthetic maps for testing ADAS features. These maps are computer-graphics-based and provide a highly detailed representation of road networks, landmarks, lane markings, junctions, signals, and traffic features.
In this blog, we will explore the importance of virtual testing and the role synthetic maps play in this while touching upon some of the constraints and challenges that their use poses.
Constraints with Real-Time Testing of AV software stacks
Real-time testing of autonomous vehicles presents significant challenges. Conducting tests in live environments often involves:
- High Costs: Setting up and maintaining real-world testing facilities, vehicles, and safety personnel can be prohibitively expensive because it includes the different levels of testing.
- Limited Coverage: Autonomous vehicles testing in specific locations or a particular geographic area may not replicate the diversity of driving conditions, terrains, speeds and weather patterns.
- Safety Concerns: Testing in live traffic introduces risks to both the vehicle and surrounding road users. Since the AV is behaving according to the scenario.
- Time-Intensive Processes: Real-world testing cycles are lengthy, slowing down the development, and time delay for the next fixed feature testing and iteration of algorithms.
Virtual Testing of AV software stacks and the role of synthetic maps
Virtual testing is an emerging transformative approach to overcome the challenges – of real-world testing. It allows developers to create controlled, repeatable, and scalable environments that simulate real-world conditions using different simulators.
Synthetic maps play a major role in effective virtual testing. They provide a highly accurate and detailed representation of real-world driving conditions, enabling realistic simulations using different simulators like Carla, Carmaker, VTD, etc. The vehicle can be tested with a given scenario which can be defined with various conditions and rules.
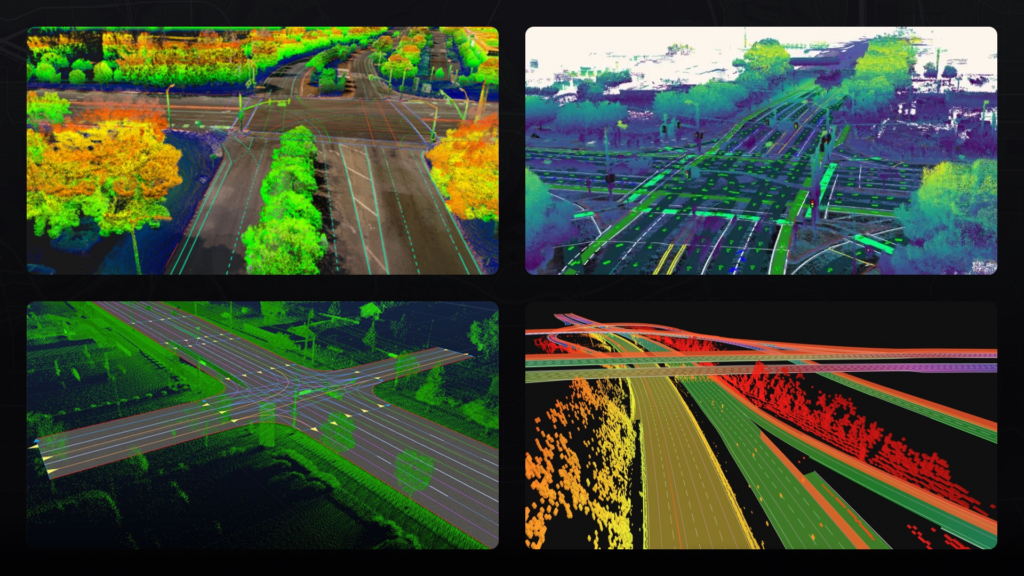
What Makes Synthetic Maps Special?
- Lane-Level Accuracy: Detailed information about lane widths, markings, junctions, speed limits, and stencils.
- Semantic Layers: Comprehensive data on objects like traffic signals, pedestrian crossings, and roadside barriers.
- 3D Representation and Elevations: Models of elevation changes, real-world elevation data, curves, and inclines.
- Dynamic Updates: Real-time changes such as construction sites, buildings, petrol areas, or roadblocks are reflected in the maps.
Advantages of Synthetic Maps for ADAS Testing
Synthetic maps provide a digital representation of real-world road networks and traffic behaviors, enabling highly accurate virtual testing environments. Integrating synthetic maps with simulators provides a high level of accuracy, allowing vehicles to be tested in various real-world scenarios., Synthetic maps significantly reduce development time while enhancing scalability to simulate roads and regulations from different regions, making them ideal for global adaptability.
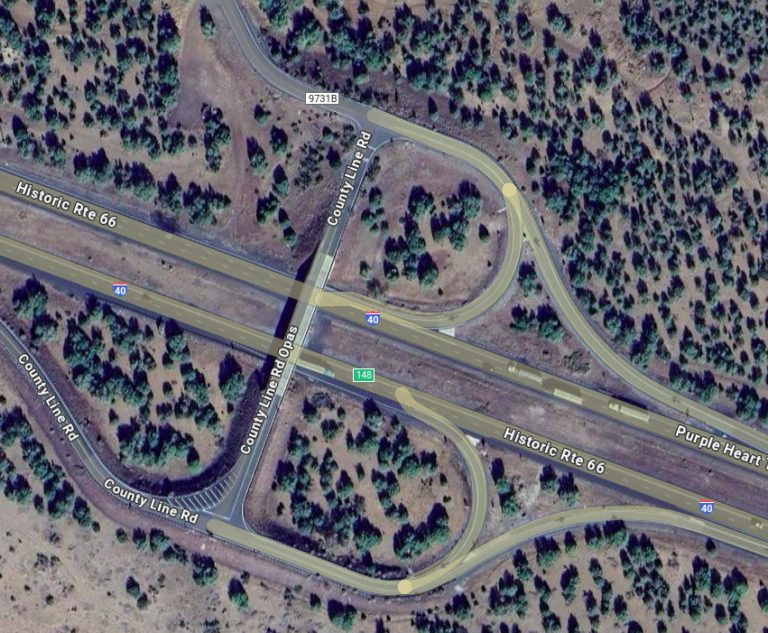
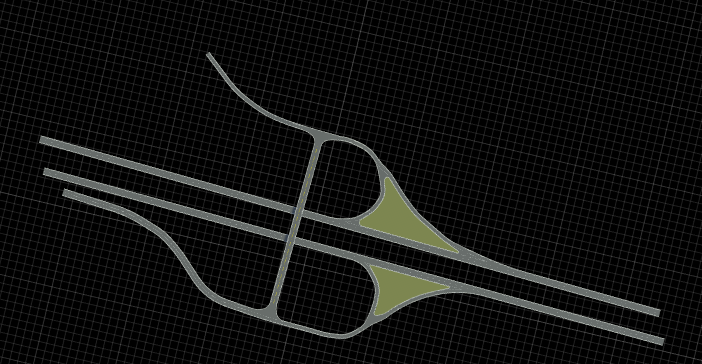
Example of Real World Data Map – Reference – Partial Cloverleaf in Dallas – Link

Optimizing Testing: The Synergy of Synthetic Maps and Simulators
The integration of synthetic maps with different simulators like CARLA, CARMAKER, VTD, etc ..allows for effective autonomous vehicle testing. Here’s how this topology works.
- Accuracy in Simulations: Synthetic maps allow developers to mirror real-world conditions, enabling rigorous testing of ADAS and autonomous features with different algorithms and automations.
- Risk-Free Testing: High-risk scenarios can be tested without damaging the lives, ensuring safety protocols are met before real-world deployment.
- Global Applicability: Virtual testing environments can replicate conditions from various regions, ensuring vehicles perform consistently worldwide.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: Simulators use the synthetic maps to reduce costs and time associated with physical tests while enabling faster innovation cycles.
Conclusion
Synthetic maps are transforming the landscape of ADAS and autonomous vehicle development by enabling real-world virtual testing. Precise, realistic, and scalable synthetic maps add to the testing fidelity in virtual environments, reducing costs, improving safety, and allowing for higher testing reliability and coverage.
To understand what we are doing in the space, write to us at sales@vayavyalabs.com or reach out to us here.
