Introduction:
The rapid evolution of connected vehicles and autonomous driving technology has significantly transformed the automotive industry. However, as digitalization and connectivity increase, so do cybersecurity risks. Modern vehicles rely heavily on software, communication networks, and electronic control units (ECUs), making them vulnerable to cyber threats.
Cyberattacks on vehicles can lead to catastrophic consequences, including loss of human lives, financial damages, operational disruptions, and data breaches. To mitigate these risks, ISO 21434, an international standard for automotive cybersecurity, provides a structured framework to evaluate and manage cybersecurity risks.
This guide delves into Impact Rating and Attack Feasibility in automotive cybersecurity, helping industry professionals understand how to assess and counter potential cyber threats effectively.
Impact Rating: Assessing the Consequences of an Automotive Cyberattack
Impact ratings assess the severity of a cyberattack on a vehicle or fleet. The impact is categorized into four primary areas:
1.1 Safety Impact (Risk to Human Lives)
Cyberattacks that compromise the safety of vehicle occupants or pedestrians are the most critical concerns. These attacks can directly affect braking systems, steering, acceleration, and other essential safety features.
Impact Levels & Examples:
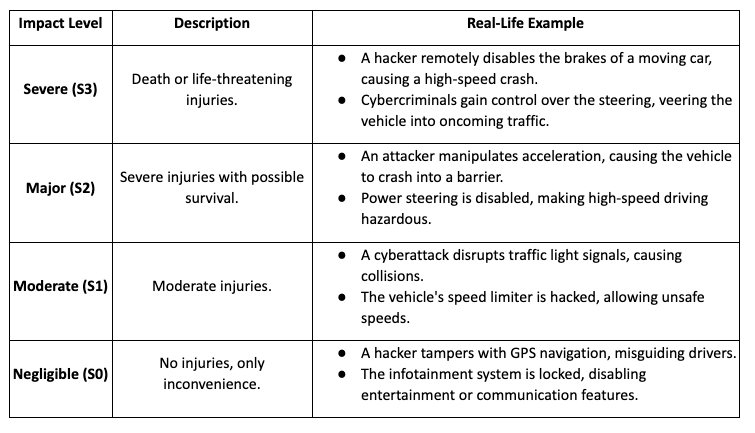
Key Insights:
- Software-based attacks targeting infotainment systems usually result in negligible impacts.
- Physical control system attacks on steering and brakes are among the most dangerous cybersecurity risks
1.2 Financial Impact (Cost of an Attack)
Cyberattacks can lead to major financial losses, including vehicle damage, lawsuits, and fleet-wide disruptions.
Impact Levels & Examples:
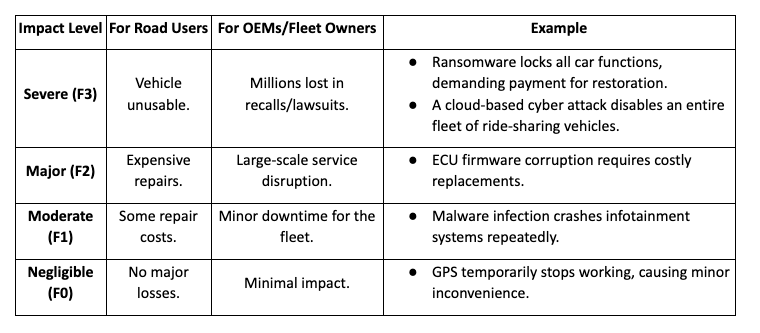
Key Insights:
- Cloud-based cyberattacks on fleets pose severe financial risks.
- Ransomware has the potential to cause major disruptions and financial damage.
1.3 Operational Impact (Effect on Vehicle & Fleet Functionality)
Cyberattacks can make individual vehicles or entire fleets inoperable.
Impact Levels & Examples:
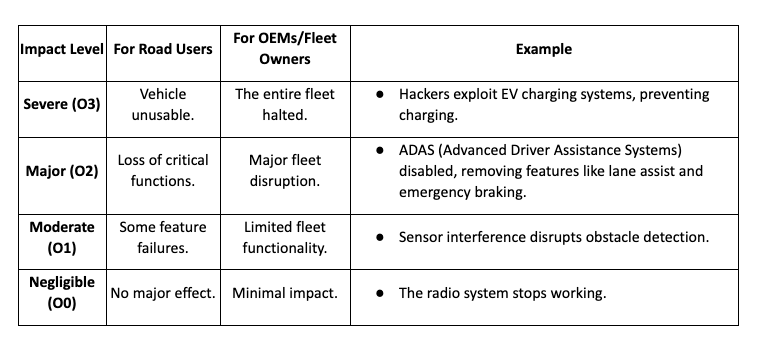
Key Insights:
- Remote attacks on ignition and charging systems are severe.
- Navigation hacks may cause inconvenience but usually don’t lead to critical failures.
1.4 Privacy Impact (Data Breaches & Exposure)
Modern vehicles store vast amounts of user data, making them prime targets for cybercriminals.
Impact Levels & Examples:
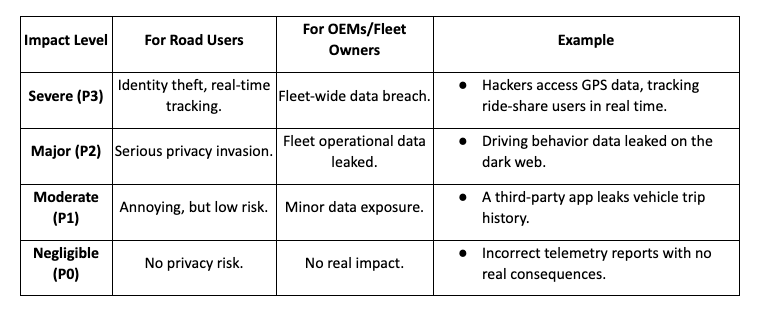
Key Insights:
- Remote attacks on ignition and charging systems are severe.
- Navigation hacks may cause inconvenience but usually don’t lead to critical failures.
Attack Feasibility: How Easy Is it to Hack a Car?
Attack feasibility determines how difficult it is for an attacker to execute a cyberattack. It is assessed based on five key factors:
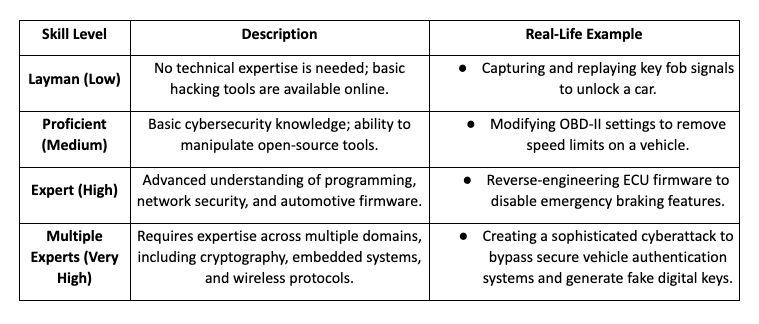
2.1 Specialist Expertise (Skill Level Required)
The level of expertise required for a successful cyberattack varies based on the complexity of the target system and the attack method.
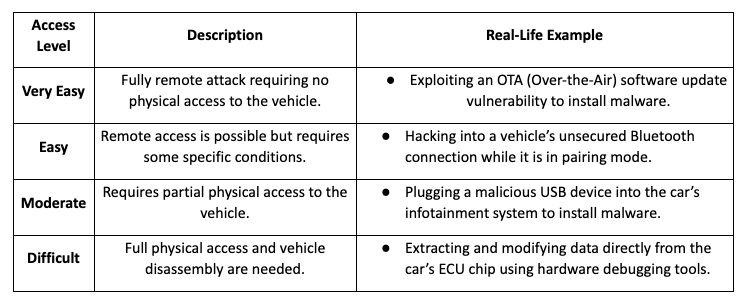
2.2 Window of Opportunity (Ease of Access)
The ease with which an attacker can gain access to the target system significantly impacts the feasibility of an attack.
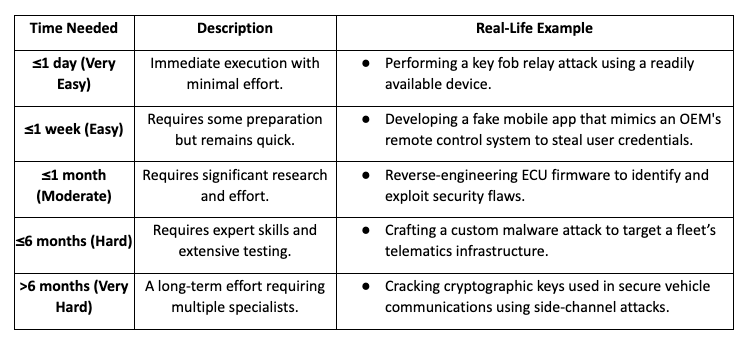
2.3 Elapsed Time (How Long the Attack Takes?)
The time required to develop and execute an attack varies based on the complexity of the attack method.
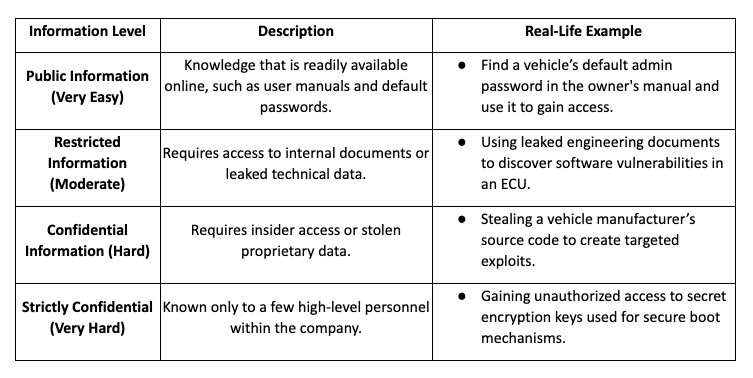
2.4 Knowledge of the Item (How Much Information is Needed?)
The amount of information required to execute an attack depends on how well-protected the vehicle’s security mechanisms are.
2.5 Equipment Required (Tools Needed for the Attack)
The type of equipment required determines the level of sophistication of the attack.
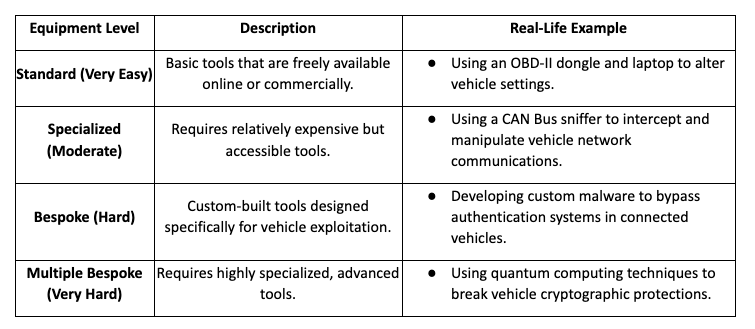
Attack Feasibility vs. Impact Assessment
A structured risk assessment methodology is critical in identifying, analyzing, and mitigating cybersecurity threats in automotive systems. To standardize this evaluation, we use a Risk Matrix that maps the feasibility of an attack against its potential impact.
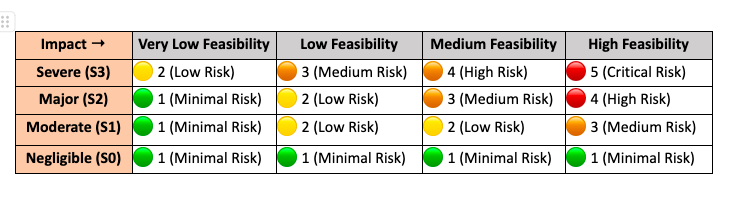
Risk Level Interpretation
- 🟢 1 (Minimal Risk): No immediate cybersecurity action is required.
- 🟡 2 (Low Risk): Consider security controls if feasible.
- 🟠 3 (Medium Risk): Security controls recommended to reduce risk.
- 🔴 4 (High Risk): Mitigations required as per ISO 21434.
- 🔴 5 (Critical Risk): Immediate risk mitigation necessary—may require system redesign.
The Future of Automotive Cybersecurity
As vehicles become increasingly connected, the attack surface expands, making it essential to adopt robust cybersecurity measures. Understanding Impact Rating and Attack Feasibility is crucial for manufacturers, regulators, and security professionals to protect vehicles, users, and data from evolving cyber threats.
Proactive cybersecurity strategies, including penetration testing, AI-driven threat detection (AI-powered security systems analyze real-time vehicle data to detect, predict, and mitigate cyber threats before they cause harm), and blockchain-based authentication (provides tamper-proof, decentralized, and transparent security by ensuring that all data transactions (e.g., software updates, authentication, vehicle-to-vehicle communications) cannot be altered or forged.), will significantly secure future vehicles by ensuring real-time threat detection, preventing unauthorized access, and maintaining the integrity of critical vehicle functions. As cyber threats evolve, integrating these advanced technologies will be crucial in mitigating risks, protecting user data, and ensuring the safety of autonomous and connected vehicles.
Cybersecurity in automotive is not optional—it is essential.
If you’re eager to explore the exciting frontiers of Automotive Cybersecurity and Functional Safety in Automotive and more about our groundbreaking initiatives in ADAS, reach out to us!
